
Study of Prevalence And Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Acinetobacter Species Isolated From Various Clinical Specimens in Tertiary Care Institute in North west Region of Rajasthan
Authore(s) : Geeta Tinna || Associate ProfessorDept. of MicrobiologySPMC BikanerRajasthanIndia
Volume : (3), Issue : 211, April - 2017
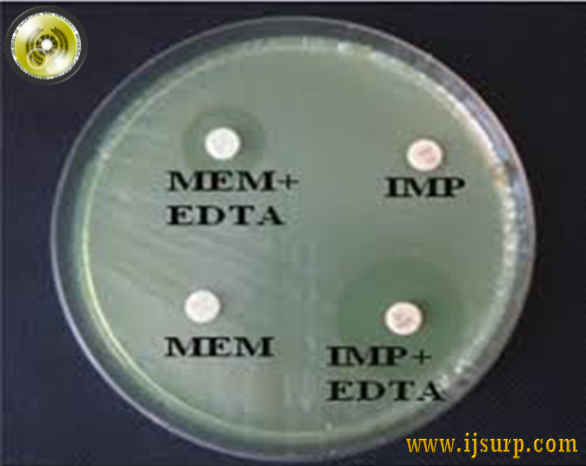
Abstract : Acinetobacter species are the fast emerging agents of opportunistic and nosocomial infections with evolving drug resistance which have become a real problem in hospital setups, particularly in critical care units. The study presented in this paper was planned with this background to have a comprehensive approach to these infections. A total of 700 patients were studied in this study. A questionnaire was developed to assess risk factors associated with development of these infections and their antimicrobial susceptibility pattern. A proper assessment of these infections along with their anti resistance pattern that predispose to these infections and the prudent use of antibiotics may help in reduction of these infections.
Keywords :Acinetobacter species, risk factors, antimicrobial susceptibility pat tern, Rajasthan.
Article: Download PDF Journal DOI : 2364/2018
Cite This Article:
Acinetobacter Species Isolated From Various Clinical Specimens in Tertiary Care Institute in North west Region of Rajasthan
Vol.I (3), Issue.I 211
Article No : 10084
Number of Downloads : 100
References :
Gautam V, Singhal L, Ray P. Burkholoderia cepacia complex : Beyond Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter. Ind J Med Microbiol 2011; 29:4-12.
Castle M, Tenney JH, Weinstein MP, Eickhoff TC. Outbreak of a multiply resistant Acinetobacter in a surgical intensive care unit : epidemiology and control. Heart Lung 1978; 7:641-4.
Chastre J, Trouillet JL, Vaugnat A, JolyGuillou ML. Nosocomial infections caused by Acinetbacter spp. Microbiology,... More
- Gautam V, Singhal L, Ray P. Burkholoderia cepacia complex : Beyond Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter. Ind J Med Microbiol 2011; 29:4-12.
- Castle M, Tenney JH, Weinstein MP, Eickhoff TC. Outbreak of a multiply resistant Acinetobacter in a surgical intensive care unit : epidemiology and control. Heart Lung 1978; 7:641-4.
- Chastre J, Trouillet JL, Vaugnat A, JolyGuillou ML. Nosocomial infections caused by Acinetbacter spp. Microbiology, Epidemiology, Infections, Management. Danvers: CRC press, 1996:117-132.
- Forster DH, Daschner FD. Acinetobacter species as nosocomial pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol InfectDis 1998;17:73-7.
- Miller GH, Sabatelli FJ, Hare RS, et al. The most Frequent aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms changes with time and geographic area : a reflection of aminoglycoside usage patterns? Aminoglycoside Resistance Study Groups. Clin Infect Dis 1997;24 (Suppl 1):S46-S62.
- Dijkshroon L, Nemec A, Seifert H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multi drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007; 5: 939-951.
- Lortholary O, Fagon JY, Hoi AB, et al. Nosocomial acquisition of multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: risk factors and prognosis. Clin Infect Dis 1995;20: 790-6.
- Baraibar J, Correa H, Mariscal D, Gallego M, Valles J, Rello J. Risk factors for infection by Acinetobacter baumannii in intubated patients with nosocomial pneumonia.Chest 1997;112:1050-4.
- Patrick RM. Manual of Clin Microbiol 2007. 29th ed, Asm Press, Washington D.C., USA. [10] National Committee of Clinical Laboratory Standards (2005) : Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 15th informational supplement. vol. 26, supplement 16, 2006.
... Less
- Gautam V, Singhal L, Ray P. Burkholoderia cepacia complex : Beyond Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter. Ind J Med Microbiol 2011; 29:4-12.
- Castle M, Tenney JH, Weinstein MP, Eickhoff TC. Outbreak of a multiply resistant Acinetobacter in a surgical intensive care unit : epidemiology and control. Heart Lung 1978; 7:641-4.
- Chastre J, Trouillet JL, Vaugnat A, JolyGuillou ML. Nosocomial infections caused by Acinetbacter spp. Microbiology, Epidemiology, Infections, Management. Danvers: CRC press, 1996:117-132.
- Forster DH, Daschner FD. Acinetobacter species as nosocomial pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol InfectDis 1998;17:73-7.
- Miller GH, Sabatelli FJ, Hare RS, et al. The most Frequent aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms changes with time and geographic area : a reflection of aminoglycoside usage patterns? Aminoglycoside Resistance Study Groups. Clin Infect Dis 1997;24 (Suppl 1):S46-S62.
- Dijkshroon L, Nemec A, Seifert H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multi drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007; 5: 939-951.
- Lortholary O, Fagon JY, Hoi AB, et al. Nosocomial acquisition of multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: risk factors and prognosis. Clin Infect Dis 1995;20: 790-6.
- Baraibar J, Correa H, Mariscal D, Gallego M, Valles J, Rello J. Risk factors for infection by Acinetobacter baumannii in intubated patients with nosocomial pneumonia.Chest 1997;112:1050-4.
- Patrick RM. Manual of Clin Microbiol 2007. 29th ed, Asm Press, Washington D.C., USA. [10] National Committee of Clinical Laboratory Standards (2005) : Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 15th informational supplement. vol. 26, supplement 16, 2006.






