
Consumption Habits in Morocco and Their Influencing Factors
Authore(s) : Rachida Belloute || Biology DepartmentMoulay Ismail UniversityB.P. 11201ZitouneMeknesMorocco,
Volume : (3), Issue : 211, January - 2019
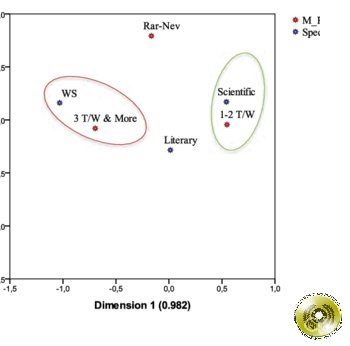
Abstract : The main objective of this study is to describe eating habits in relation with some influencing factors and to determine the current trends of consumer behavior. It is based on a structured questionnaire with a sample of 100 respondents. The results obtained show that food rhythms of respondents used to be structured. Meals were taken at home with family at a steady pace. Currently, the constraint of time and the work schedule result in irregular eating habits such as skips of meal and high frequency of outside consumption. Consumers do not seem conscious of their diets; the choice of meals consumed outside is based primarily on pleasure. The meals are not diversified. They tend to be high in meat and low in vegetables and fish. These behaviors are influenced by several factors and reflect a nutritional transition to which women and people having a high level of education, especially scientists, are relatively resistant.
Keywords :choice, preference, meal, food.
Article: Download PDF Journal DOI : 2364/2018
Cite This Article:
Consumption Habits in Their Influencing Factors
Vol.I (3), Issue.I 211
Article No : 10022
Number of Downloads : 108
References :
Seignalet, J. (2012), “L'alimentation ou la troisième médecine”, éditions du Rocher, Collection : Equilibre, pp. 1-770.
Apfelbaum, M., and Romon, M. (2009), “Additifs alimentaires”, Diététique et nutrition (7ème édition), 470-486.
Gallen, C., and Pla J. (2013), “Allergie et intolérance aux additifs alimentaires”, Revue française d’allergologie, 53, S9-S18.
Sauvage, C. (2010), “Controverse... More
- Seignalet, J. (2012), “L'alimentation ou la troisième médecine”, éditions du Rocher, Collection : Equilibre, pp. 1-770.
- Apfelbaum, M., and Romon, M. (2009), “Additifs alimentaires”, Diététique et nutrition (7ème édition), 470-486.
- Gallen, C., and Pla J. (2013), “Allergie et intolérance aux additifs alimentaires”, Revue française d’allergologie, 53, S9-S18.
- Sauvage, C. (2010), “Controverse l’hypersensibilité aux additifs alimentaires est une réalité clinique : pour”, Revue française d’allergologie, 50, 288–291.
- Remesy, C. (2006), “Produits frais, produits bruts… la base incontournable d’une alimentation saine”, Journal de pédiatrie et de pué- riculture, 19, 192-193.
- Fleischer, G. (2006), “Les produits chimiques utilisés en agriculture – sont-ils nécessaires ou superflus?”, Agriculture & développement rural, 1, 51-54.
- Benjelloun, S., Bade, E., and Razès, M. (2011), “Profil Nutritionnel du Maroc”, Division de la nutrition et de la protection des consommateurs, FAO, 1-57.
- Benjelloun, S. (2002), “Nutrition transition in Morocco”. Public Health Nutrition, 5 (1A), 135-140.
- El Rhazi, K., Nejjari, C., Berraho, A., Abda, N., Zidouh, A. and Rekkali B. (2009), “Prévalence de l’obésité et les principaux facteurs sociodémographiques associés au Maroc”, Revue d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, 57 (S1), S25.
- Sebbani, M., Elbouchti, I., Adarmouch, L. and Amine, M. (2013), “Prevalence of obesity and overweight among children in primary schools in Marrakech, Morocco”, Revue d'Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique, 61 (6), 545–549.
- Soualem,A., Ahami, A., Aboussaleh, Y., Elbouhali, B., andBonthoux, F. (2008), “Le comportement alimentaire des préadolescents en milieu urbain au nord-ouest du Maroc”, Revue Francophone de Clinique Comportementale et Cognitive, 13 (4), 39-46.
- Aboussad, A., Cherkaoui, M., and Vimard, P. (2010), “Santé et vulnérabilités au Maroc”, 1er Edition, Imprimerie et Papeterie El Watanya, Marrakech, 1-256.
- Meulman, J.J., and Heiser, W. J. (2011), IBM SPSS Catégories 20, Manuel. IBM Corporation 1989, 1- 325, [Online] Available: URL: http://ibm-spss-statistics.soft32.com/.
- Core Team, R. (2014), “R: A language and environment statistical computing”. R. foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Autriche, [Online] Available: URL: http://www. R-project.org/.
- Morrison, D.F. (1978), “Multivariate Statistical Methods”, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, Singapore, 415p.
- Benzecri, J.P., and Benzecri, F. (1983), “La pratique de l’analyse des données”, Tome 1, Analyse des Correspondances, exposé élémentaire, Paris: Dunod.
- Stafford,J., and Bodson, P. (2006), “L’analyse multivariée avec SPSS, presses de l’université de Québec 258 p.
- Bertrand, R. (1986), “Pratique de l’analyse statistique des données”, Sainte-Foy, presses de l’université de Québec,379 p.
- Kan, K ., andTsai, W.D. (2004), “Obesity and risk knowledge”, J Health Econ, 23(5), pp. 907-934.
- Fulkerson, J.A., Rydell, S. (2008), “Family meals: Perceptions of benefits and challenges amoug parents of 8 to 10 year-old children Journal of American Dietetic Association, 108, 706-709.
- Houbaida, M. (2008), “ Le Maroc végétarien, 15ème -18ème siècles: Histoire et biologie ”, éditions Wallada, Casablanca, 149 p.
- Bang, H.O. ,Dyerberg, J., Nielsen, A.B.E. (1971), “plasma lipid and lipoprotein pattern in greenlandic west-coast es- kimos”, The Lancet , 297 (7710) ,1143 – 1146.
- Rizos, E.C., Ntzani, E.E., Bika, E., Kostapanos, M.S., and Elisaf, M.S. (2012), “Association between omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and risk of major cardiovascular disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis”, The Journal of American Medical Association,308 (10),1024–1033.
- Hooper, L., Thompson, R.L., Harrison, R.A., Summerbell, C.D., Ness, A.R., Moore, H.J., Worthington, H.V., Durrington, P.N., Higgins, J.P., Capps, N.E., Riemersma, R.A., Ebrahim, S.B., and Davey Smith, G. (2006), “Risks and benefits of omega 3 fats for mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review”, British Medical Journal, 332(7544), 752-760.
... Less
- Seignalet, J. (2012), “L'alimentation ou la troisième médecine”, éditions du Rocher, Collection : Equilibre, pp. 1-770.
- Apfelbaum, M., and Romon, M. (2009), “Additifs alimentaires”, Diététique et nutrition (7ème édition), 470-486.
- Gallen, C., and Pla J. (2013), “Allergie et intolérance aux additifs alimentaires”, Revue française d’allergologie, 53, S9-S18.
- Sauvage, C. (2010), “Controverse l’hypersensibilité aux additifs alimentaires est une réalité clinique : pour”, Revue française d’allergologie, 50, 288–291.
- Remesy, C. (2006), “Produits frais, produits bruts… la base incontournable d’une alimentation saine”, Journal de pédiatrie et de pué- riculture, 19, 192-193.
- Fleischer, G. (2006), “Les produits chimiques utilisés en agriculture – sont-ils nécessaires ou superflus?”, Agriculture & développement rural, 1, 51-54.
- Benjelloun, S., Bade, E., and Razès, M. (2011), “Profil Nutritionnel du Maroc”, Division de la nutrition et de la protection des consommateurs, FAO, 1-57.
- Benjelloun, S. (2002), “Nutrition transition in Morocco”. Public Health Nutrition, 5 (1A), 135-140.
- El Rhazi, K., Nejjari, C., Berraho, A., Abda, N., Zidouh, A. and Rekkali B. (2009), “Prévalence de l’obésité et les principaux facteurs sociodémographiques associés au Maroc”, Revue d'Epidémiologie et de Santé Publique, 57 (S1), S25.
- Sebbani, M., Elbouchti, I., Adarmouch, L. and Amine, M. (2013), “Prevalence of obesity and overweight among children in primary schools in Marrakech, Morocco”, Revue d'Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique, 61 (6), 545–549.
- Soualem,A., Ahami, A., Aboussaleh, Y., Elbouhali, B., andBonthoux, F. (2008), “Le comportement alimentaire des préadolescents en milieu urbain au nord-ouest du Maroc”, Revue Francophone de Clinique Comportementale et Cognitive, 13 (4), 39-46.
- Aboussad, A., Cherkaoui, M., and Vimard, P. (2010), “Santé et vulnérabilités au Maroc”, 1er Edition, Imprimerie et Papeterie El Watanya, Marrakech, 1-256.
- Meulman, J.J., and Heiser, W. J. (2011), IBM SPSS Catégories 20, Manuel. IBM Corporation 1989, 1- 325, [Online] Available: URL: http://ibm-spss-statistics.soft32.com/.
- Core Team, R. (2014), “R: A language and environment statistical computing”. R. foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Autriche, [Online] Available: URL: http://www. R-project.org/.
- Morrison, D.F. (1978), “Multivariate Statistical Methods”, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, Singapore, 415p.
- Benzecri, J.P., and Benzecri, F. (1983), “La pratique de l’analyse des données”, Tome 1, Analyse des Correspondances, exposé élémentaire, Paris: Dunod.
- Stafford,J., and Bodson, P. (2006), “L’analyse multivariée avec SPSS, presses de l’université de Québec 258 p.
- Bertrand, R. (1986), “Pratique de l’analyse statistique des données”, Sainte-Foy, presses de l’université de Québec,379 p.
- Kan, K ., andTsai, W.D. (2004), “Obesity and risk knowledge”, J Health Econ, 23(5), pp. 907-934.
- Fulkerson, J.A., Rydell, S. (2008), “Family meals: Perceptions of benefits and challenges amoug parents of 8 to 10 year-old children Journal of American Dietetic Association, 108, 706-709.
- Houbaida, M. (2008), “ Le Maroc végétarien, 15ème -18ème siècles: Histoire et biologie ”, éditions Wallada, Casablanca, 149 p.
- Bang, H.O. ,Dyerberg, J., Nielsen, A.B.E. (1971), “plasma lipid and lipoprotein pattern in greenlandic west-coast es- kimos”, The Lancet , 297 (7710) ,1143 – 1146.
- Rizos, E.C., Ntzani, E.E., Bika, E., Kostapanos, M.S., and Elisaf, M.S. (2012), “Association between omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and risk of major cardiovascular disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis”, The Journal of American Medical Association,308 (10),1024–1033.
- Hooper, L., Thompson, R.L., Harrison, R.A., Summerbell, C.D., Ness, A.R., Moore, H.J., Worthington, H.V., Durrington, P.N., Higgins, J.P., Capps, N.E., Riemersma, R.A., Ebrahim, S.B., and Davey Smith, G. (2006), “Risks and benefits of omega 3 fats for mortality, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review”, British Medical Journal, 332(7544), 752-760.






